Introduction
The pharmacy profession stands at the cusp of a significant transformation. Technological advancements, particularly in artificial intelligence (AI) and automation, are reshaping healthcare delivery. As these technologies become more integrated into pharmacy practice, certain traditional roles are at risk of becoming obsolete within the next five years.

This article identifies five pharmacy roles likely to face obsolescence soon and offers strategies for pharmacists to adapt and thrive in this new landscape.
I. Traditional Dispensing Pharmacists
Automation Impact: Rise of Automated Dispensing Systems
Automated dispensing systems are revolutionizing how medications are prepared and delivered. Machines like robotic pill dispensers and automated compounding devices can handle tasks with greater speed and accuracy than humans.
Potential Obsolescence Risk within 5 Years: 70%
These systems reduce medication errors, improve inventory management, and free up pharmacists to focus on more patient-centered services.
Future Outlook: Shift Towards Clinical Roles Over Dispensing
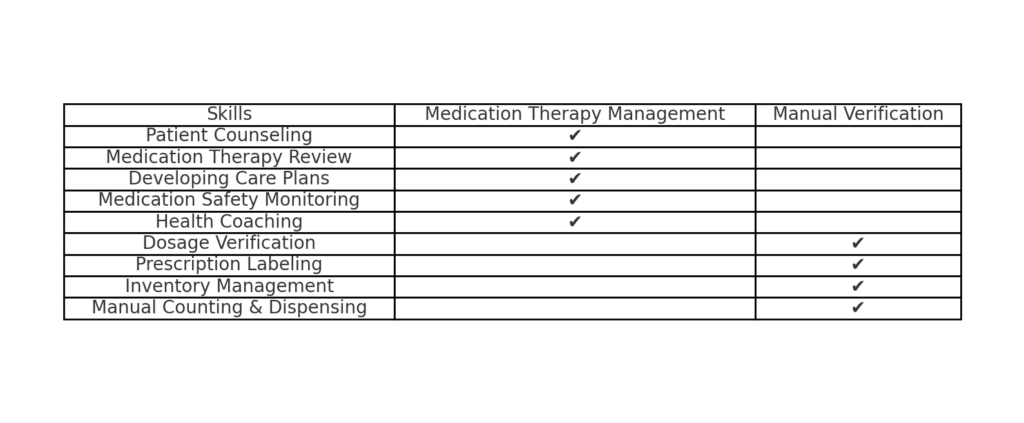
Pharmacists can pivot towards clinical roles that emphasize direct patient care. By focusing on medication therapy management, disease state management, and patient counseling, pharmacists can provide value that automation cannot replicate.

II. Manual Prescription Verification
AI in Verification: Introduction of AI Algorithms for Accuracy
AI algorithms are increasingly used to verify prescriptions, check for drug interactions, and ensure appropriate dosing. These systems can process vast amounts of data quickly and with high accuracy.
Potential Obsolescence Risk within 5 Years: 65%
By reducing the reliance on human verification, pharmacies can streamline operations and minimize errors due to fatigue or oversight.
Role Transition: Moving from Verification to Medication Therapy Management
Pharmacists should develop expertise in medication therapy management, where their clinical judgment and patient relationships are invaluable. This shift allows them to oversee complex medication regimens and collaborate with other healthcare professionals.
III. Inventory Management Specialists
Inventory Technology: Implementation of IoT and Automated Tracking
The Internet of Things (IoT) enables real-time tracking of pharmaceutical inventories. Automated systems can monitor stock levels, predict demand, and reorder supplies without human intervention.
Potential Obsolescence Risk within 5 Years: 80%
These technologies improve efficiency and reduce costs associated with overstocking or stockouts.
Career Shift: Focusing on Supply Chain Optimization
Pharmacists can specialize in supply chain optimization, ensuring that the procurement processes meet regulatory standards and ethical sourcing requirements.
IV. Drug Information Retrieval Roles
Access to Information: Use of Digital Databases and AI Assistants
Digital databases and AI assistants provide instant access to drug information, interactions, and evidence-based guidelines.
Potential Obsolescence Risk within 5 Years: 60%
These tools have made manual retrieval roles less necessary, as healthcare providers can access information directly. There is also potential for the consumer to access information easily, especially price-sensitive consumers looking for ways to save.
Evolving Responsibilities: Emphasis on Interpreting Data Rather Than Retrieving It
Pharmacists should focus on interpreting complex data to make clinical decisions, tailoring information to individual patient needs.
V. Medication Reconciliation Technicians
Integrated EHR Systems: Seamless Data Sharing Across Platforms
Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems are becoming more integrated, allowing automatic updates and sharing of patient medication histories across healthcare providers.
Potential Obsolescence Risk within 5 Years: 75%
This integration reduces the need for manual reconciliation of medications during patient transitions.
New Opportunities: Patient Education and Care Coordination
Pharmacists can transition into roles that focus on patient education about medication adherence, side effects, and lifestyle modifications.
Conclusion
Adaptation Strategies: Importance of Upskilling and Embracing New Technologies
To remain relevant, pharmacists must embrace continuous learning and adapt to technological advancements. Upskilling in areas such as data analytics, pharmacogenomics, and patient-centered care is essential.
Call to Action: Encouraging Proactive Career Development
Pharmacists should proactively seek opportunities to expand their skill sets. By anticipating industry changes, they can position themselves as indispensable members of the healthcare team.