In the intricate ecosystem of healthcare, Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) play a pivotal role in shaping medication distribution and pricing. For pharmacists, understanding the functions and impact of PBMs is essential to navigate the complexities of modern pharmacy practice effectively. This knowledge not only enhances operational efficiency but also empowers pharmacists to provide optimal patient care. By delving into the role of PBMs, their functions, the controversies surrounding them, and strategies to engage with them, pharmacists can better position themselves as indispensable information dispensers in a dynamic healthcare landscape.
Role of PBMs: Key Players in Medication Distribution and Pricing
Pharmacy Benefit Managers serve as intermediaries between pharmacies, insurers, and drug manufacturers. Their primary role is to manage prescription drug benefits on behalf of health insurers, employers, and other payers. PBMs negotiate with drug manufacturers to secure discounts and rebates, develop formularies that determine which medications are covered, and process prescription drug claims. By leveraging their bargaining power, PBMs aim to control drug costs and ensure that patients have access to necessary medications at affordable prices. Below is my favorite figure that represents the industry’s dynamics.
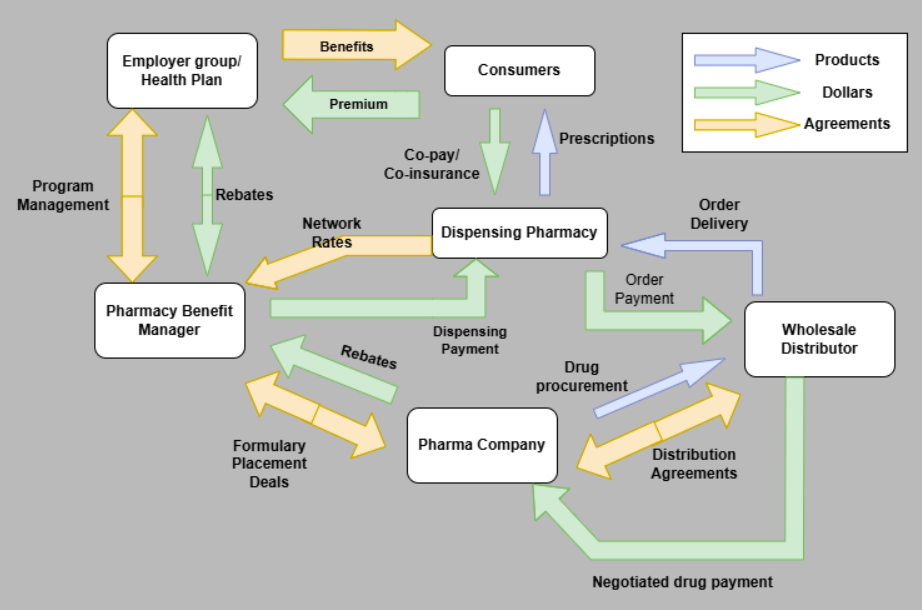
PBMs also implement utilization management strategies, such as prior authorization and step therapy, to optimize medication use and promote cost-effective treatment options. Additionally, they provide valuable data analytics and reporting services to stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making and improving overall healthcare outcomes.
Impact on Pharmacy Practice: Influence on Operations and Patient Care
The influence of PBMs on pharmacy practice is profound, affecting various aspects of operations and patient care. PBMs establish reimbursement rates for pharmacies, which directly impact the financial viability of pharmacy operations. These reimbursement rates are often subject to negotiations and can vary based on factors such as pharmacy network participation and performance metrics.
Furthermore, PBMs influence medication availability through formulary management. By determining which drugs are covered and at what tier, PBMs guide prescribing patterns and influence patient access to specific medications. Pharmacists must navigate these formularies to ensure that patients receive appropriate and cost-effective therapies, often requiring collaboration with prescribers to identify suitable alternatives when necessary.
PBMs also play a role in patient adherence programs, offering support services that encourage patients to follow their prescribed treatment plans. By facilitating access to medications and providing educational resources, PBMs contribute to improved health outcomes and enhanced patient satisfaction.
I. Functions of PBMs
Negotiation: Securing Discounts and Rebates
One of the core functions of PBMs is negotiating discounts and rebates with pharmaceutical manufacturers. PBMs leverage their substantial purchasing power to secure favorable pricing agreements, which can lead to significant cost savings for payers and, ultimately, patients. These negotiations often involve complex contracts that stipulate terms such as volume-based discounts, tiered pricing structures, and performance-based incentives.
By securing these discounts, PBMs help reduce the overall cost of prescription drugs, making medications more accessible and affordable for patients. Additionally, the savings achieved through these negotiations can be reinvested into programs that enhance patient care, such as medication therapy management and adherence initiatives.
Formulary Management: Deciding Covered Medications
Formulary management is another critical function of PBMs, involving the selection and maintenance of a list of approved medications that are covered by a particular insurance plan. This formulary serves as a guide for both prescribers and patients, outlining which drugs are preferred and the associated cost-sharing requirements.
PBMs develop formularies based on various criteria, including clinical efficacy, safety profiles, cost-effectiveness, and therapeutic value. By carefully curating these lists, PBMs aim to ensure that patients have access to high-quality medications while controlling overall drug expenditure. Pharmacists must stay informed about formulary changes and updates to provide accurate guidance to patients and collaborate with prescribers to optimize medication therapy.
II. Controversies and Criticisms
Transparency Issues: Lack of Clarity in Pricing Structures
Despite their significant role in managing drug benefits, PBMs have faced criticism regarding transparency in their pricing structures. Critics argue that the intricate nature of PBM contracts and rebate agreements obscures the true cost of medications, making it difficult for stakeholders to understand how savings are achieved and distributed.
This lack of transparency can lead to mistrust among pharmacies, patients, and even payers, as the exact mechanisms by which PBMs influence drug pricing remain unclear. Addressing these transparency concerns is crucial for fostering trust and ensuring that all parties involved can make informed decisions based on accurate and comprehensible information.
Impact on Drug Costs: Effects on Patients and Pharmacies
The impact of PBMs on drug costs is a subject of ongoing debate. While PBMs are designed to lower medication costs through negotiations and formulary management, some argue that their practices can inadvertently contribute to rising drug prices. For instance, the rebate system may incentivize the use of higher-priced drugs, as manufacturers offer larger rebates to gain favorable formulary placement.
This dynamic can result in higher out-of-pocket costs for patients, particularly those who do not benefit directly from the rebates negotiated by PBMs. Additionally, pharmacies may experience reduced reimbursement rates, which can affect their profitability and sustainability. Balancing the need to control drug costs with ensuring fair reimbursement for pharmacies is a critical challenge that PBMs must address to maintain a harmonious healthcare ecosystem.
III. Navigating PBM Relationships
Contract Management: Understanding Terms and Conditions
Effective contract management is essential for pharmacies to navigate their relationships with PBMs successfully. Understanding the terms and conditions outlined in PBM contracts is crucial for ensuring fair reimbursement rates, compliance with formulary requirements, and adherence to performance metrics.
Pharmacists should carefully review contract provisions related to reimbursement formulas, fee structures, and any penalties or incentives tied to performance outcomes. Engaging with legal and financial advisors can help pharmacies negotiate favorable terms and mitigate potential risks. Clear communication and transparency in contractual agreements foster stronger partnerships and facilitate smoother operations within the managed care framework.
Advocacy: Engaging in Policy Discussions
Pharmacists have a vital role to play in advocacy efforts aimed at shaping policies and regulations that govern PBMs. By participating in policy discussions, pharmacists can influence reforms that promote transparency, fair reimbursement practices, and equitable access to medications.
Engaging with professional organizations, such as the American Pharmacists Association (APhA), allows pharmacists to collectively voice their concerns and propose solutions to address the challenges posed by PBMs. Advocacy efforts can lead to meaningful changes that enhance the role of pharmacies in the healthcare system and ensure that patient care remains the primary focus.
IV. Strategies for Pharmacies
Diversification: Reducing Reliance on PBM Reimbursements
Diversifying revenue streams is a strategic approach for pharmacies to reduce their dependence on PBM reimbursements. By expanding services beyond traditional prescription dispensing, pharmacies can enhance their financial stability and resilience against fluctuations in PBM policies.
Value-added services such as medication therapy management, immunizations, chronic disease management, and wellness programs not only generate additional income but also strengthen the pharmacist-patient relationship. Diversification empowers pharmacies to offer comprehensive care, differentiate themselves in a competitive market, and maintain profitability despite changes in PBM reimbursement structures.
Patient Engagement: Assisting Patients with PBM-Related Issues
Active patient engagement is crucial for addressing PBM-related challenges and improving medication access. Pharmacists can play a key role in assisting patients navigate complex PBM processes, such as prior authorization requirements and formulary restrictions.
By providing personalized support, pharmacists help patients understand their prescription benefits, identify alternative therapies, and advocate for necessary medication coverage. Additionally, educating patients about the role of PBMs and how to effectively communicate with their insurance providers empowers them to take an active role in managing their healthcare, leading to better adherence and health outcomes.
V. Future Trends
Regulatory Changes: Potential Reforms Affecting PBMs
The regulatory landscape for PBMs is continually evolving, with potential reforms aimed at increasing transparency, curbing anti-competitive practices, and ensuring fair reimbursement rates. Legislative efforts at both the federal and state levels are focusing on measures to disclose PBM pricing structures, eliminate hidden fees, and promote competition within the industry.
Pharmacists must stay informed about these regulatory changes to anticipate their impact on pharmacy practice and adapt accordingly. Understanding upcoming reforms allows pharmacies to align their operations with new requirements, advocate for favorable policies, and leverage opportunities presented by a changing regulatory environment.
Industry Shifts: Emergence of New Models
The healthcare industry is witnessing the emergence of new models that challenge the traditional PBM framework. Direct-to-consumer pharmacy models, vertical integration of pharmacies and PBMs, and the rise of technology-driven solutions are reshaping the landscape of pharmacy benefit management.
These shifts present both opportunities and challenges for pharmacies. Embracing innovative models can enhance operational efficiency, improve patient access to medications, and foster collaborative relationships with other healthcare stakeholders. Staying abreast of industry trends enables pharmacists to adapt their practices, leverage new technologies, and maintain a competitive edge in the evolving healthcare ecosystem.
Conclusion
Staying Informed: Importance of Ongoing Education
In the rapidly changing world of pharmacy benefit management, staying informed is paramount. Continuous education on PBM functions, regulatory developments, and industry trends equips pharmacists with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of managed care effectively. Engaging in professional development opportunities, attending industry conferences, and participating in educational programs ensure that pharmacists remain adept at addressing the challenges and leveraging the opportunities presented by PBMs.
Collaborative Efforts: Working Towards Fair Practices
Fostering collaborative efforts among pharmacists, PBMs, policymakers, and other healthcare stakeholders is essential for promoting fair and transparent practices within the managed care framework. By working together, these groups can develop solutions that enhance medication access, ensure equitable reimbursement, and prioritize patient care.
Pharmacists, as trusted healthcare providers, are uniquely positioned to advocate for changes that benefit both patients and the pharmacy profession. Collaborative initiatives can lead to the implementation of best practices, the development of standardized metrics, and the creation of a more transparent and efficient pharmacy benefit management system.
Embracing the Value of PBMs in the Healthcare Ecosystem
Pharmacy Benefit Managers are integral to the healthcare ecosystem, facilitating the distribution and pricing of medications in a manner that aims to balance cost control with patient access. While controversies surrounding transparency and drug costs persist, the collaborative relationship between pharmacists and PBMs can generate significant value for all stakeholders involved.
By understanding the functions of PBMs, navigating contractual relationships effectively, and implementing strategic initiatives, pharmacists can harness the benefits of PBMs to enhance their practice and improve patient outcomes. Embracing the role of PBMs as partners rather than adversaries fosters a cooperative environment where the shared goal of optimal patient care is achieved.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, pharmacists who remain informed, engaged, and proactive in their interactions with PBMs will be well-positioned to thrive. By leveraging their expertise and advocating for fair practices, pharmacists can ensure that PBMs contribute positively to the delivery of high-quality, accessible, and affordable healthcare.